Leased line provides a layer 1 service by delivering bits between the devices connected to the leased line. It is the layer 2 protocol that control and use leased lines. The most popular data link layer protocols for leased lines are High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) and Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). Here we briefly talk about HDLC as an example WAN data link protocol.
High Level Data Link Control (HDLC) protocol is a group of protocols for transmitting synchronous data Packets between Point-to-Point nodes. Basically it was developed for point to point topology where only two nodes exist -- sending node and receiving node. Once a HDLC frame exits from sending node it has only one place to go -- the receiving node. Taking advantage of this fact, HDLC's addressing is really easy -- it don't need address at all; HDLC frame, however has a legacy address field due to the fact that telcos company historically used to include more than 2 nodes in their circuit, before HDLC is dedicated only to Point to Point leased line.
The contents of an IOS’s HDLC frame are shown in the following table. Notice the Data field has a variable length. The Layer 3 packets are encapsulated inside the Data field. Routers need to be pre-configured, so that both sending and receiving nodes know what type of layer 3 packets are encapsulated in the data field, therefore only 1 type of layer 3 packet is allowed. Note that the end flag of one frame may be (but does not have to be) the beginning (start) flag of the next frame.
| Flag | Address | Control | Data | FCS | Flag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| new frame start | receiver | legacy | only one type of layer 3 packet allowed | error dectction | frame end |
Because of the above limitation of IOS's HDLC, cisco routers use a proprietary HDLC frame. The cisco HDLC added a type field to indicate what type of layer 3 packet is encapsulated in the Data field, allowing multiple network layer protocols to share the same serial link.
The contents of an cisco proprietary HDLC frame are shown in the following table:
| Flag | Address | Control | type | Data | FCS | Flag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| new frame start | receiver | legacy | layer 3 protocol type | multiple layer 3 packet allowed | error dectction | frame end |
When an IP packet from source PC needs to travel across WAN to reach destination PC, the IP packet has to be de-encapsulated and re-encapsulated between Ethernet frame and HDLC frame.
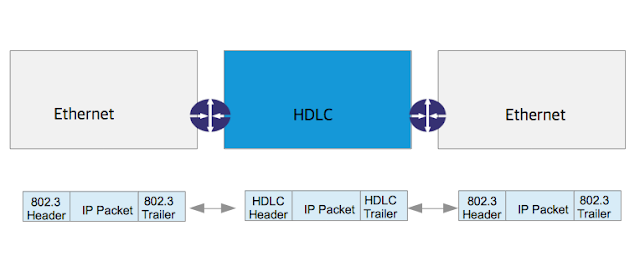 |
| IP packet travel LAN and WAN |
At the beginning, the sending node encapsulates the IP packet in an Ethernet frame with the destination MAC address of the gateway router. This Ethernet frame travels across the LAN and reaches the gateway router. At the gateway router, the Ethernet frame is de-encapsulated to extract the IP packet. This IP packet is then encapsulated in an HDLC frame and forward to the leased line WAN network. The HDLC frame travels across leased line WAN and reaches other side of the point to point link, which is the receiving LAN's gateway router. The HDLC frame is de-encapsulated to extract the IP packet. This IP packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the destination MAC address as the receiving node. Finally the Ethernet frame travels across the LAN and reaches the receiving node.
No comments:
Post a Comment